いろいろ chapter 40 nuclear fission and fusion exercises 283950-Chapter 40 nuclear fission and fusion exercises answers
Fission and fusion are two processes that alter the nucleus of an atom Nuclear fission provides the energy in nuclear power plants and fusion is the source of the sun's energy The use of fission in power plants can help conserve fossil fuelsChapter Section Problem 1A The Atomic Nucleus And Radioactivity Chapter 40 Nuclear Fission And Fusion and a wide range of conceptdevelopment questions and exercises Application Reinforce and apply key concepts with handson laboratory work, critical thinking, and problem solving More Editions of This BookThe electromagnetic force acts as a disruptive force in large nuclei, creating repulsions which help in fission The electromagnetic force, although disruptive at long range, is attractive at short range and helps keep small nuclei together The strong force is shortrange, and therefore of no major importance in nuclear energy considerations
Frontiers Mitochondrial Dynamics Imbalance A Strategy For Promoting Viral Infection Microbiology
Chapter 40 nuclear fission and fusion exercises answers
Chapter 40 nuclear fission and fusion exercises answers-Explain the fission concept in the context of fusion bombs, the production of energy by the Sun, and nucleosynthesis The process of combining lighter nuclei to make heavier nuclei is called nuclear fusion As with fission reactions, fusion reactions are exothermic—they release energy Suppose that we fuse a carbon and helium nuclei toCh 40 Nuclear Fission and Fusion Study Guide STUDY PLAY ____ forces inside a nucleus contribute to nuclear instability Electrical The splitting of atomic nuclei is called?



Http Www Angelfire Com Fl4 Kevin Physics2 Ch40f Pdf
US scientists introduce new fusion reactor concept What caught my eye here was the new concept to reduce the size of the standard fusion reactor design which relies on tokamak magnetic field plasma containment The CAT concept is described in an article published on 19 March in the journal Nuclear Fusion, and was developed from firstofakindProtons and neutrons are packed tightly in the tiny nucleus of an atom Recall that some atomic nuclei are unstable and emit nuclear radiation as they decay The stability of a nucleus depends on the nuclear forces that hold the nucleus together If like charges repel oneChapter40nuclearfissionandfusionanswers 1/2 Downloaded from elasticsearchcolumbiancom on by guest there is ample opportunity to learn characteristic numbers through the illustrative calculations and the exercises An updated Solution Manual is available to the instructor A new feature to aid the student is a set of
352 Postulates of the Special Theory of Relativity; NCERT Exercise Questions & Answers of 12th Class Physics Chapter 13 – Nuclei 12th Class Physics NCERT Solutions of Chapter 13 Nuclei available over here and they are prepared by subject experts as per the CBSE Board Guidelines You will find detailed answers to the class 12 physics textbook questions along with ch 13 nuclei exemplary problems, worksheets, and exercisesFission And Fusion 308 Chapter 10 FOCUS Objectives 1041 Compare and contrast nuclear forces 1042 Describe the process of nuclear fission 1043 Explain how nuclear reactors are used to produce energy 1044 Describe the process of nuclear fusion Build Vocabulary WordPart Analysis Remind students that they can use what they know about
A endothermic B exothermic C nuclear D chemical E radioactivity 32 The following reaction 01𝑛 𝑈→ 𝑎 3692𝐾𝑟 301𝑛 is called A Fusion B Fission C alpha decay D beta decay E gamma decay 33 The following reaction 12𝐻 13𝐻→24𝐻𝑒01𝑛 is called• nuclear reactions in stars CHAPTER 11 Nuclear Chemistry 110 Introduction 115 Nuclear Fission 111 The Nucleus 116 Nuclear Fusion 112 Nuclear Reactions and Radioactivity 117 Origin of the Heavy Elements 113 Kinetics of Radioactivity 118 Chapter Summary and Objectives 114 Nuclear Radiation and Living Tissue 119 Exercises343 The Breeder Reactor;




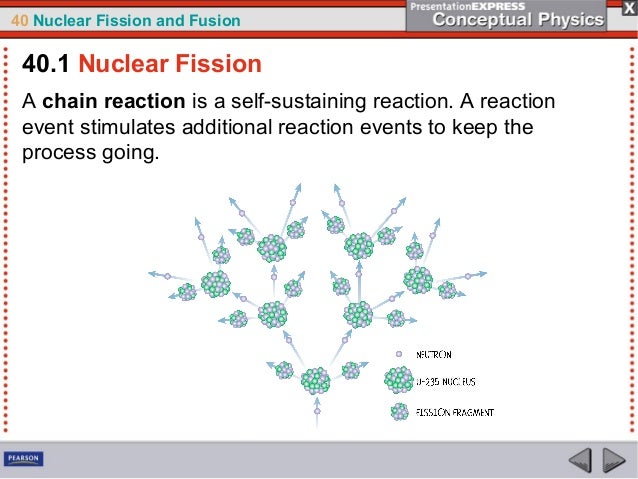
Exercises 40 1 Nuclear Fission



Fission Physics
Nuclear fission Nuclear fission occurs when repelling electrical forces overpower the attracting nuclear Nuclear Fusion Fusion is the opposite reaction of fission In fusion, atoms are fused together For a fusion reaction to occur, it is necessary to bring two nuclei so close that nuclear forces become active and glue the nuclei together Deuterium and Tritium, isotopes of hydrogen, are used in fusion reactorsNuclear Fission Examples Chernobyl Accident Difference Between Fission and Fusion What is Nuclear Reaction?



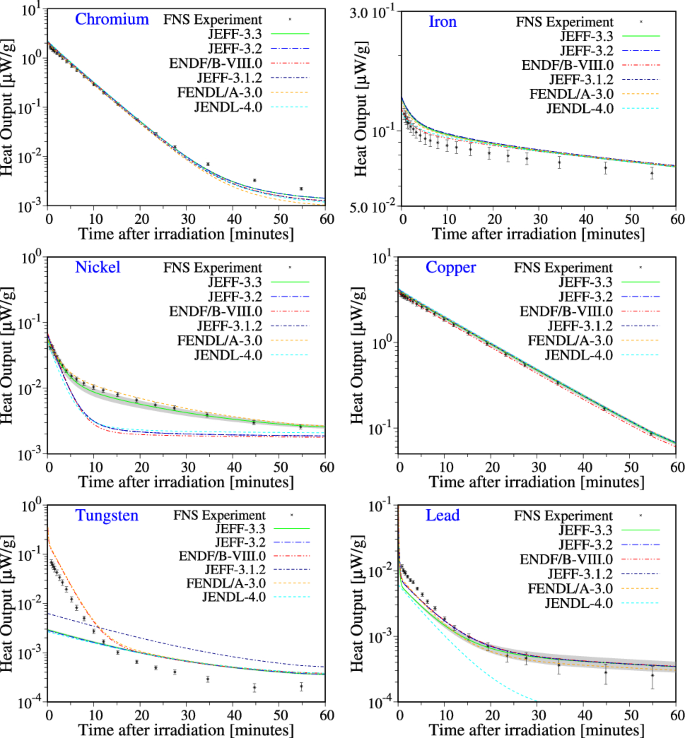
The Joint Evaluated Fission And Fusion Nuclear Data Library Jeff 3 3 Springerlink




The Economics Of Nuclear Fusion Rd Jonathan Linton
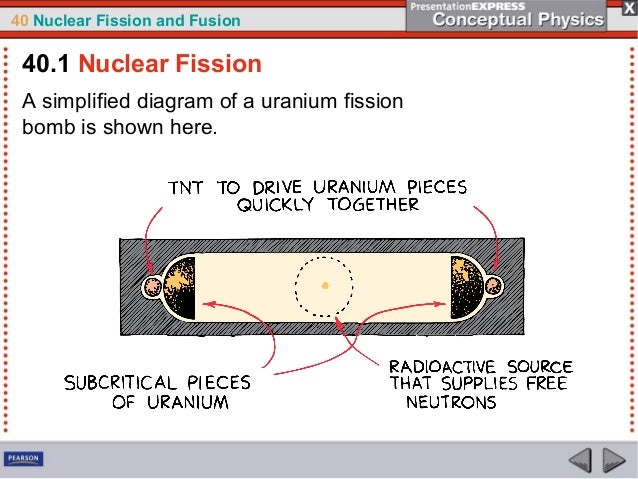
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission bomb) or from a combination of fission and fusion reactions (thermonuclear bomb) Both bomb types release large quantities of energy from relatively small amounts of matter 61 The History and Basics of FissionA The reaction splits a nucleus into lighter nuclei b The reaction joins two lighter nuclei into a heavier nucleus c The reaction is used to generate energy in a nuclearNuclear Fission and Fusion Why?




Ch40 Nuclear Fissionandfusion




Mitochondrial Fission And Fusion A Dynamic Role In Aging And Potential Target For Age Related Disease Sciencedirect
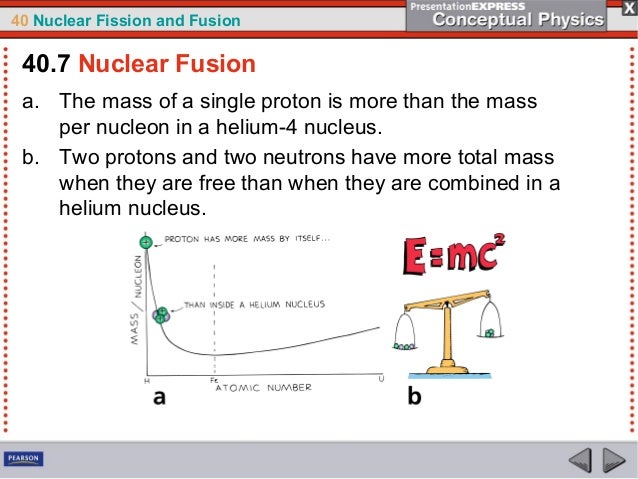
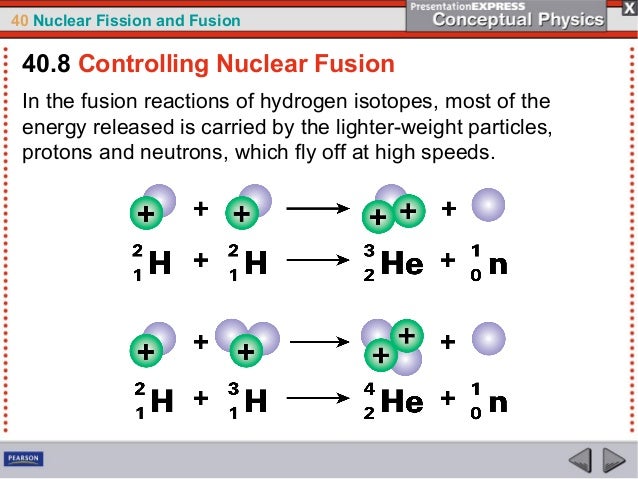
2 Is the following sentence true or false?Chapter 40 Nuclear Fission and Fusion Vocabulary Flashcards The extra mass, multiplied by the square of thespeed of light, is exactly equal to your energy input E mc2CHAPTER 40 NUCLEAR FISSION AND FUSION 817 817 Strictly speaking, the mass of Mass is congealed energy Chapter 40 Nuclear Fission And A nuclear fission reactor that not only produces power but produces more nuclear fuel than it consumes by converting a non fissionable uranium isotope into a fissionable plutonium isotope Term nuclear fusion Definition The combining of nuclei of light atoms, such as hydrogen, into heavier nuclei accompanied by the release of much energy




Settz3bvrjexum




Fission Physics
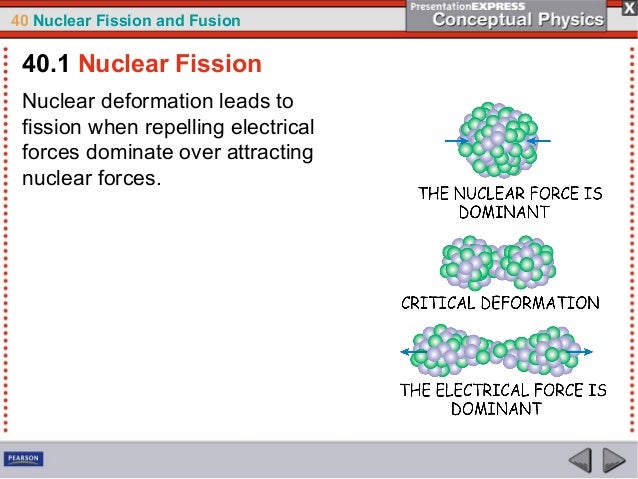
Nuclear energy The controlled harvesting of energy from fission reactions involves the controlled harvesting of energy from fission reactions The reaction can be controlled because the fission of uranium235 (and a few other isotopes, such as plutonium239) can be artificially initiated by injecting a neutron into a uranium nucleusA delicate balance between the strong force and electrical forces of repulsion exists inside a nucleusA delicate balance between the strong force and electrical forces of repulsion exists inside a nucleus 3 Circle the letter that describes why nuclear fission



Ec Europa Eu Jrc Sites Jrcsh Files Reqno Jrc647 La Na En C Pdf 5b1 5d Pdf



The Effects Of Different Doses Of Exercise On Pancreatic B Cell Function In Patients With Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Study Protocol For And Rationale Behind The Dose Ex Multi Arm Parallel Group Randomised Clinical Trial
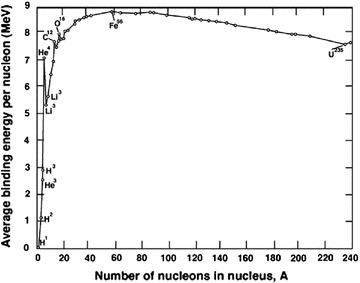
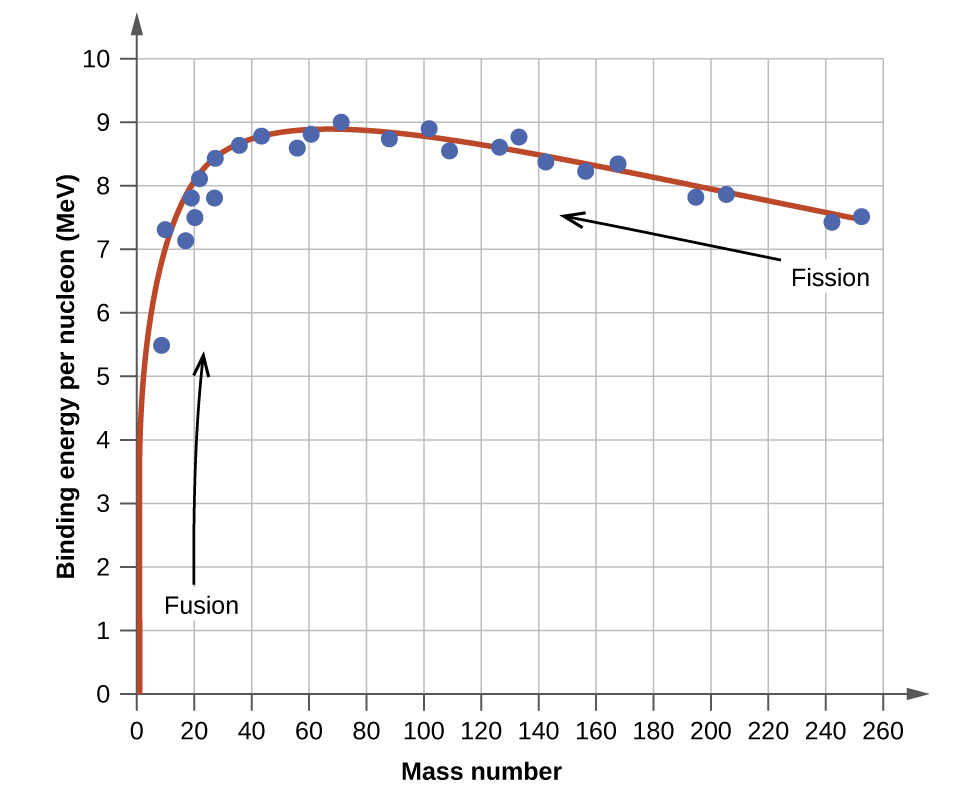
Conceptual PhysicsReading and Study Workbook N Chapter 40 347 Exercises 401 Nuclear Fission (pages 809–811) 1 What is nuclear fission?Nuclear fission and fusion involve the disintegration and combination of the elemental nucleus In the case of nuclear fission, an atom divides into two or more smaller or lighter atoms Nuclear fusion occurs when two or more atoms join or fuse together to form a large or a heavier atomNuclear binding energy is also used to determine whether fission or fusion will be a favorable process For elements lighter than iron56, fusion will release energy because the nuclear binding energy increases with increasing mass Elements heavier than iron56 will generally release energy upon fission, as the lighter elements produced




The Impact Of Exercise On Mitochondrial Dynamics And The Role Of Drp1 In Exercise Performance And Training Adaptations In Skeletal Muscle Sciencedirect



2
Chapter 40 – Nuclear Fission and Fusion 2 3 4 Fission splitting of atomic nuclei Experiments on radioactive material in the 1930's Bombarding a nucleus with a slow moving neutron Atom would split with a large release of energy n 235 n 142 Kr Ba n n Krypton Barium Three Neutrons Bombarding the Uranium atom with a single neutron would produce two lighter CHAPTER 40 NUCLEAR FISSION AND FUSION 815 405 The Breeder FIGURE 4010 ᭤ Pu239, like U235, under Reactor goes fission when it cap tures a neutronKey Termbreeder reactor 405 The Breeder Reactor᭤ Teaching Tip Explain thatgraphitemoderated reactors Know nukes before you When small amounts of Pu239 are mixed with U238 in aDownload File PDF Chapter 40 Nuclear Fission And Fusion Answers Chapter 40 Nuclear Fission And Fusion Answers As recognized, adventure as capably as experience nearly lesson, amusement, as without difficulty as settlement can be gotten by just checking out a book chapter 40 nuclear fission and fusion answers with it is not



Exercises 40 1 Nuclear Fission
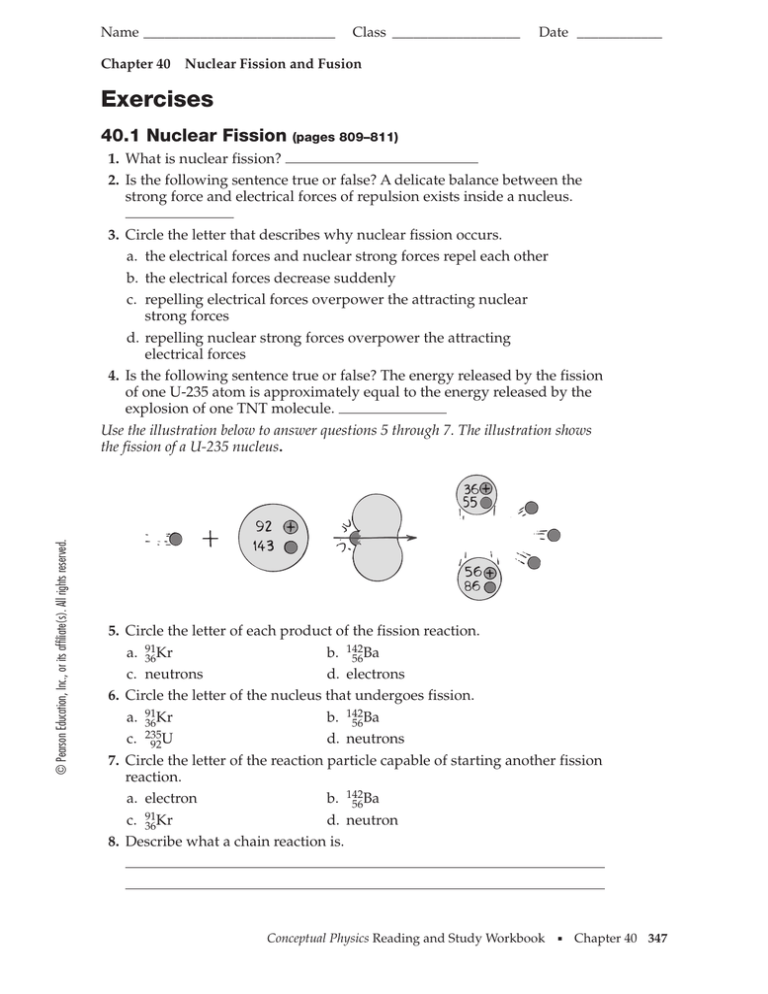



Exercises 40 1 Nuclear Fission
Learn about the basics of fission and fusion, chain reactions, nuclear reactors and nuclear weapons in this video!Balasubramanian Viswanathan, in Energy Sources, 17 Introduction In simple terms nuclear fusion is a process in which one or more light nuclei fuse together to generate a relatively heavier nucleus in which in there is some mass deficiency that is released as energy, and the quantity of energy released follows Einstein's formula E = mc 2, in which E is the energy in joules, m is theNuclear Energy Nuclear Binding Energy, Fission, and Fusion Einstein discovered that matter could be converted to energy (and viceversa) The equation that expresses this massenergy equivalency is E = mc2 (c = 300x108 m/s) or E = ( m)c2 Every process that releases energy is accompanied by an equivalent loss of mass



Http Physics Bu Edu Duffy Essentialphysics Chapter29 Chapter29 Problems Pdf




Ch40 Nuclear Fissionandfusion
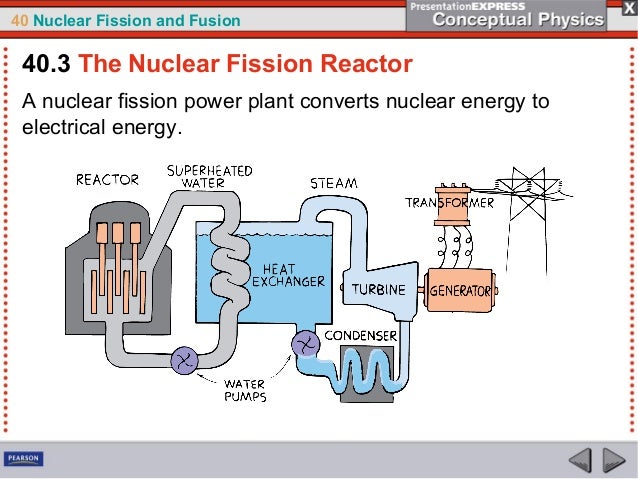
Section 253 Fission and Fusion of Atomic Nuclei 811 with ChemASAP Fission can be controlled so energy is released more slowly Nuclear reactors, such as the one illustrated in Figure 2511, use controlled fission to produce useful energy In the controlled fission reaction within a nuclear reactor, much of the energy generated is in the formNuclear Fission b The reaction joins two lighter nuclei into a heavier nucleus Nuclear Fusion c The reaction is used to generate energy in a nuclear power plant Nuclear Fission d The reaction generates radioactive waste with a long halflife Nuclear Fission 7 Complete each nuclear equation for (a) fission and (b) fusion *** aNuclear weapon A weapon that derives its energy from the nuclear reactions of either fission or fusion fusion A nuclear reaction in which nuclei combine to form more massive nuclei with the concomitant release of energy and often neutrons fission The process of splitting the nucleus of an atom into smaller particles;




Ch40 Nuclear Fissionandfusion




The Impact Of Exercise On Mitochondrial Dynamics And The Role Of Drp1 In Exercise Performance And Training Adaptations In Skeletal Muscle Sciencedirect
2 Is the following sentence true or false?Chapter 3 Unit 8 Nuclear Fission and Fusion Nuclear Fission and Fusion Nuclear fission is the splitting apart of a heavy nucleus into lighter nuclei and neutrons When a heavy nucleus of Uranium235 is bombarded with a neutron, it splits into smaller elements and few other neutronsTo make a selfsustained nuclear fission reactor with 235 U, it is necessary to slow down the neutrons Water is very effective at this, since neutrons collide with protons in water molecules and lose energy Figure 2232 shows a schematic of a reactor



The Joint Evaluated Fission And Fusion Nuclear Data Library Jeff 3 3 Springerlink




Ch40 Nuclear Fissionandfusion
Exercises 401 Nuclear Fission advertisement Name _____ Class _____ Date _____ Chapter 40 Nuclear Fission and Fusion Exercises 401 Nuclear Fission (pages 809–811) 1 What is nuclear fission?Ch 40 Physics Concepts (Nuclear Fission and Fusion) study guide by sophievelez includes 8 questions covering vocabulary, terms and more Quizlet flashcards, activities and games help you improve your grades These are homework exercises to accompany Chapter 3 of the Furman University's LibreText for CHE 101 Chemistry and Global Awareness 6E Nuclear Weapons Fission and Fusion (Exercises) Chemistry LibreTexts




4h81cbqkhhf Bm




The Economics Of Nuclear Fusion Rd Jonathan Linton
Nuclear fusion reactions that power our Sun (Photo NASA) Providing energy from nuclear fusion is widely regarded as the grand engineering challenge of the twentyfirst century Many researchers all over the world focus on ways of producing energy by recreating an artificial star on Earth Nuclear Fusion The Key to a Sustainable PlanetFossil fuels and the nuclear reactions of fission of radioactive isotopes We show that the origin of society's interest in nuclear energy lies in the fact that much more energy is released per unit mass of a nuclear fuel than per unit mass of a fossil fuel This is a mixed blessing It has led to the development of nuclear weapons (see Chapter The fragments are radioactive because of the increase number of neutrons needed to bind the nucleus together Name the combining of nuclei of light atoms into heavier nuclei accompanied by the release of much energy T or F Atomic nuclei are positively charged T – the nucleus only contains protons and neutrons




Chapter 10 Nuclear Physics Lecture Slides
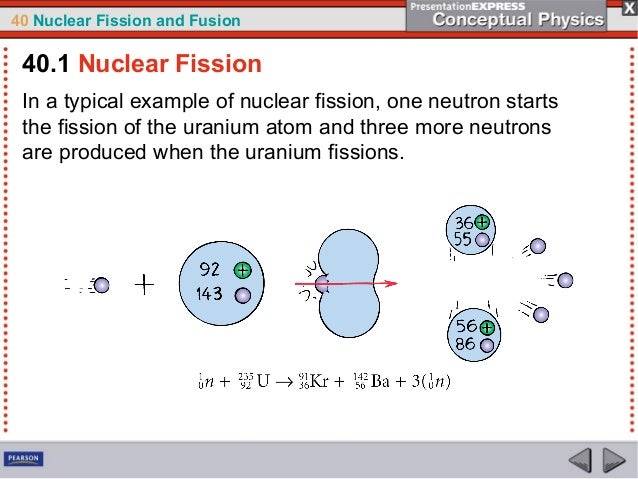



Ch40 Nuclear Fissionandfusion
Chapter 34 Nuclear Fission and Fusion 341 Nuclear Fission;ProcedureDip the end of each wand into the solution and remove Gently blow into the ring of each wand to make a bubble with a diameter a little larger than the ring, and catch the bubble on the wand Bring the wands and the bubbles together Press the bubbles together to form one large bubble, illustrating fusion342 Nuclear Fission Reactors;




Exercises 40 1 Nuclear Fission



Www Osti Gov Servlets Purl
Nuclear Fission and Fusion continued What Holds a Nucleus Together?Chapter 35 Special Theory of Relativity 351 Motion Is Relative;The reaction that involves the change in the identity or characteristics of an atomic nucleus, induced by bombarding it with an energetic particle is known as a nuclear reactionThe bombarding particle may either be an alpha particle, a gammaray photon, a




The Economics Of Nuclear Fusion Rd Jonathan Linton




Mitotic Cell Cycle Binary Fission Mitotic Cell Cycle
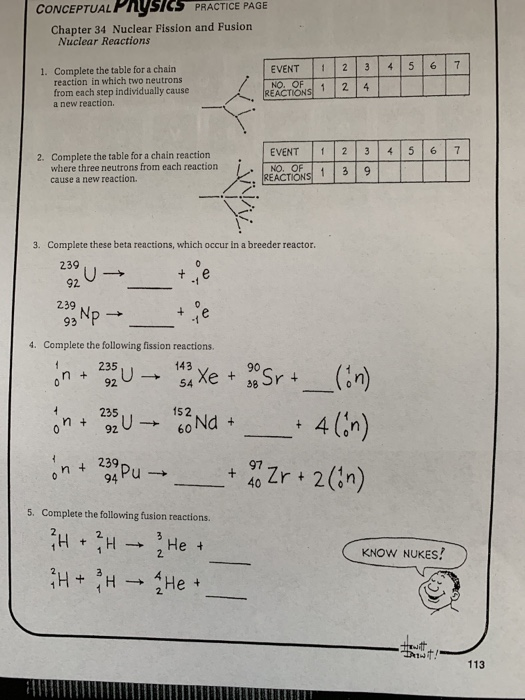
Name Nuclear Fission and Fusion Period Date ConceptDevelopment Practice Page EVENT NO OF REACTIONS 401 4 5 67 1 2 3 4, 5, Complete the table for a chainProblem 66P For which process does each statement apply—nuclear fission, nuclear fusion, both fission and fusion?258 CHAPTER 14 Nuclear fusion is essentially the antithesis of the fission process Light nuclei are combined in order to release excess binding energy and they form a heavier nucleus Fusion reactions are responsible for the energy of the sun They have also been used on earth for



Lesson Plan Nuclear Energy What S Your Reaction




Fusion Reactors An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
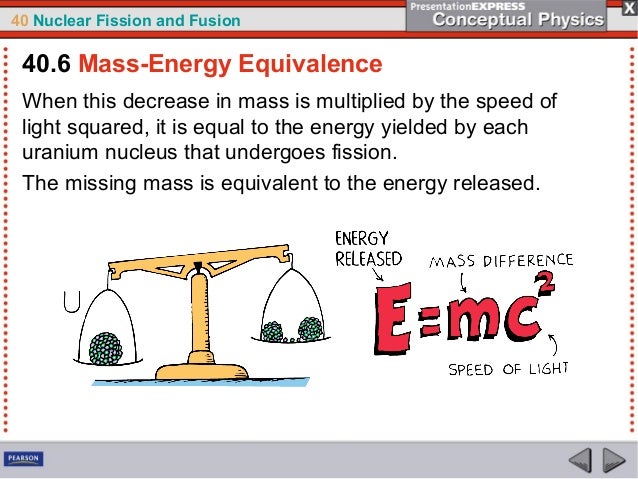



Ch40 Nuclear Fissionandfusion




Chapter 21 Lesson Starter Ppt Video Online Download




Nuclear Power Wikipedia




Ch40 Nuclear Fissionandfusion



Http Physics Bu Edu Duffy Essentialphysics Chapter29 Chapter29 Problems Pdf




40 Nuclear Fission And Nuclear Fission And Fusion A Nuclear Fission Reactor Generates Energy Through A Controlled Nuclear Fission Reaction Nuclear Bomb Is Not Possible Pdf Document
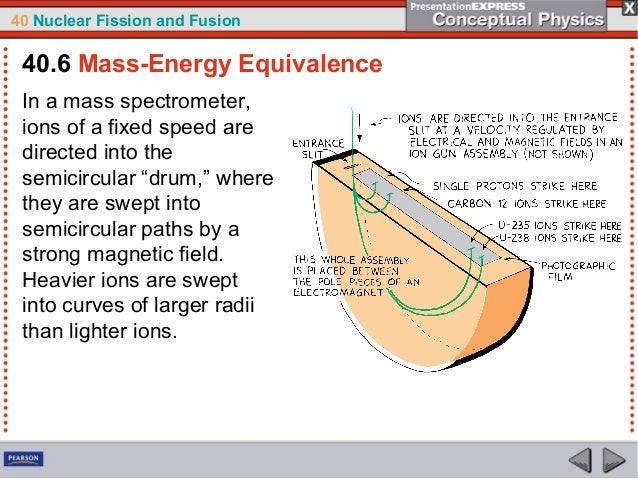



Ch40 Nuclear Fissionandfusion




Ch40 Nuclear Fissionandfusion




Fission Physics
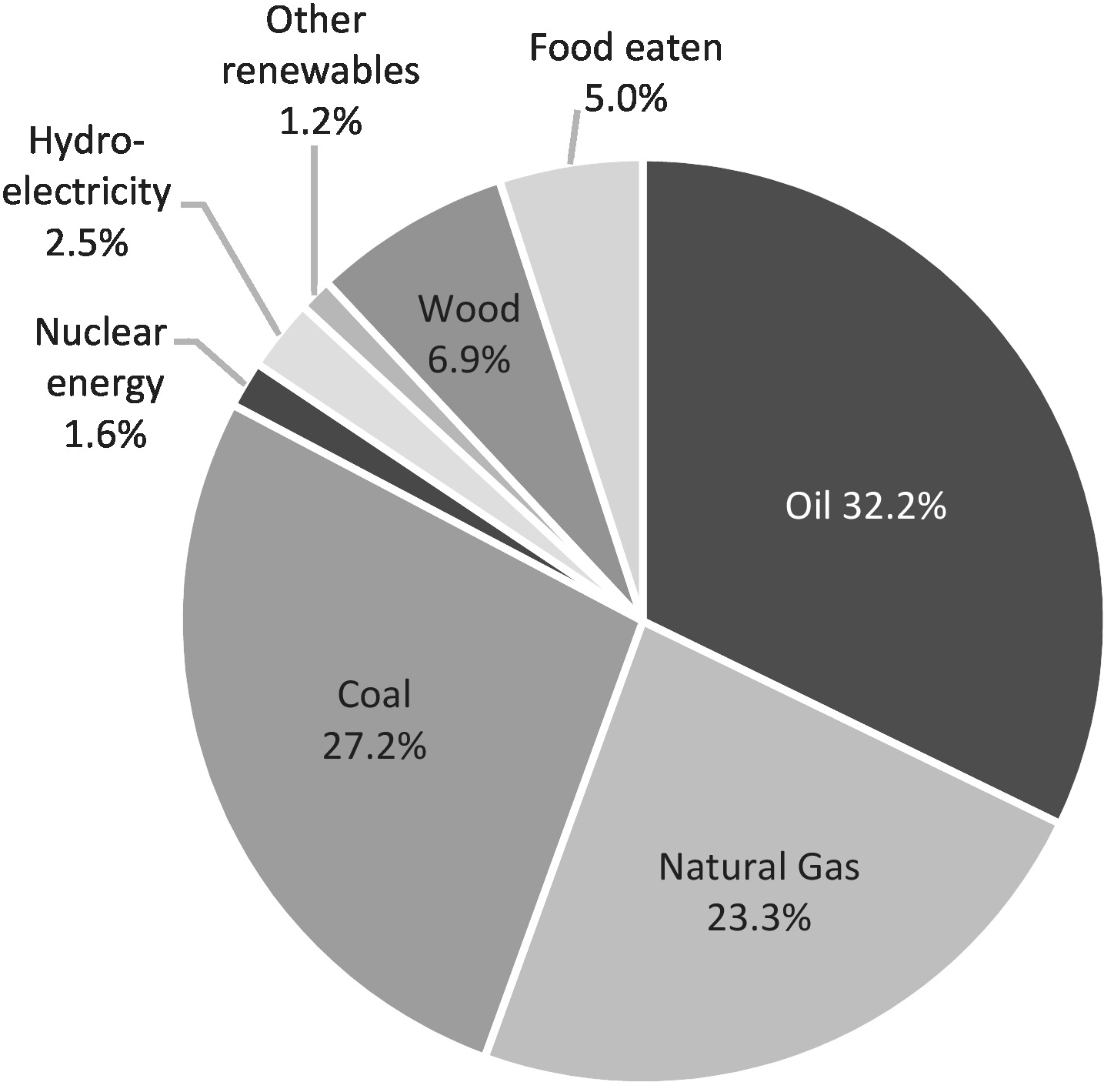



Energy Chapter 3 There Is No Planet B




Ch40 Nuclear Fissionandfusion
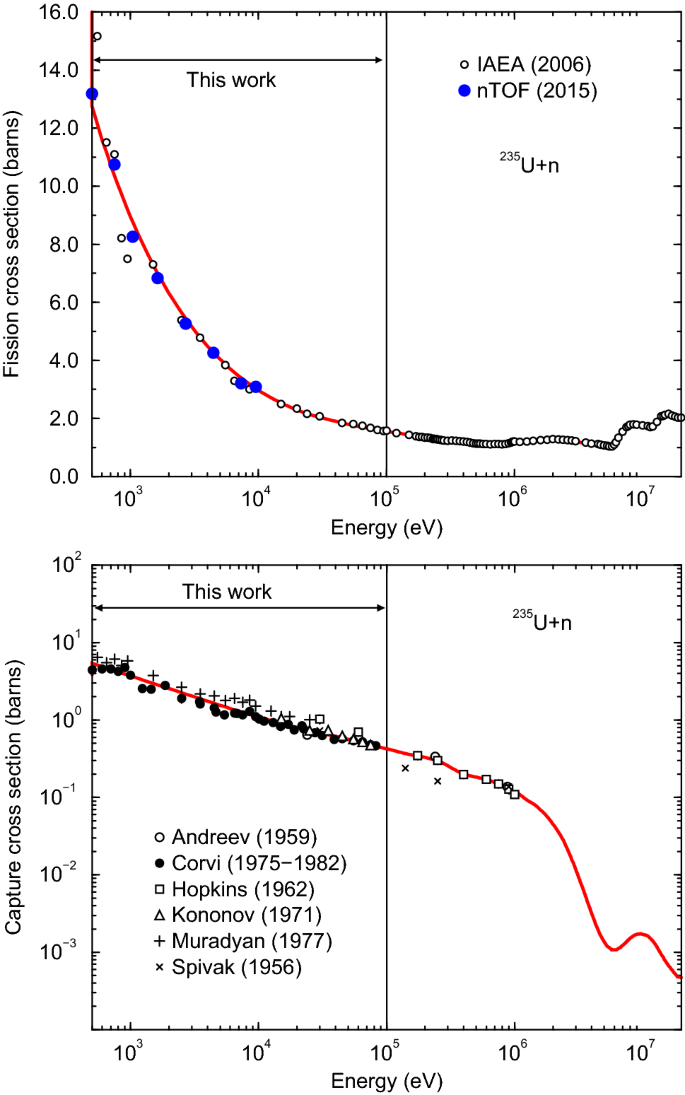



The Joint Evaluated Fission And Fusion Nuclear Data Library Jeff 3 3 Springerlink
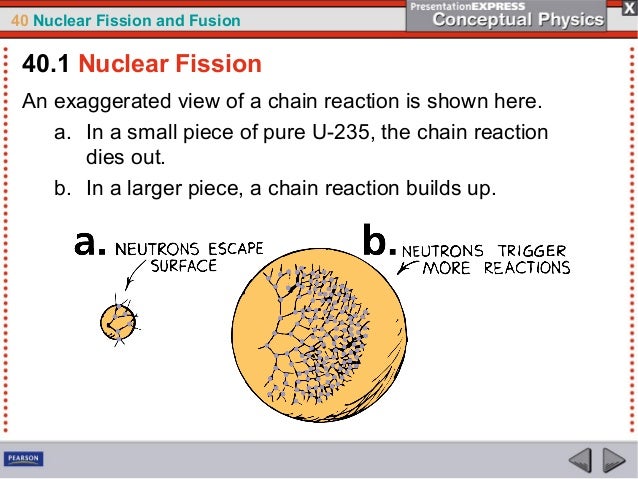



Ch40 Nuclear Fissionandfusion




Ch40 Nuclear Fissionandfusion




Ch40 Nuclear Fissionandfusion




11 5 Nuclear Energy The Basics Of General Organic And Biological Chemistry




Exercises 40 1 Nuclear Fission




Ch40 Nuclear Fissionandfusion



Http Www Cse Salford Ac Uk Physics Gsmcdonald Pp Pplatoresources H Flap P9 3t Pdf




Nuclear Fission And Fusion 40 Nuclear Mceachern High Pages 1 22 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5



2



2




Transmutation And Nuclear Energy Chemistry




The Economics Of Nuclear Fusion Rd Jonathan Linton




Transmutation And Nuclear Energy Chemistry



Fliphtml5 Com Syiy Atqo Basic




Mitochondrial Fission And Fusion A Dynamic Role In Aging And Potential Target For Age Related Disease Sciencedirect



Ch40 Nuclear Fissionandfusion




Ebook University Physics With Modern Physics Chapters 1 40




40 Nuclear Fission And Fusion Nuclear Fission And



Ch40 Nuclear Fissionandfusion




Nuclear Fission And Fusion 40 Nuclear Mceachern High Pages 1 22 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5



Ch40 Nuclear Fissionandfusion




6 E Nuclear Weapons Fission And Fusion Exercises Chemistry Libretexts




Frontiers Mitochondrial Dynamics Imbalance A Strategy For Promoting Viral Infection Microbiology




Ch40 Nuclear Fissionandfusion




Nuclear Fission And Fusion 40 Nuclear Mceachern High Pages 1 22 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5




Nuclear Fission And Fusion Ch 40 By Isaac Vega




The Economics Of Nuclear Fusion Rd Jonathan Linton



The Joint Evaluated Fission And Fusion Nuclear Data Library Jeff 3 3 Springerlink



Ch40 Nuclear Fissionandfusion



Conceptual P Practice Page Chapter 34 Nuclear Fission Chegg Com




Fission Physics



2




Ch40 Nuclear Fissionandfusion



Ch40 Nuclear Fissionandfusion




Ch40 Nuclear Fissionandfusion




Chapter 40 Nuclear Fission And Chapter 40 Nuclear Fission And Fusion 2 3 4 Fission Pdf Document




Ch40 Nuclear Fissionandfusion




Ch40 Nuclear Fissionandfusion




France



The Joint Evaluated Fission And Fusion Nuclear Data Library Jeff 3 3 Springerlink




The Impact Of Exercise On Mitochondrial Dynamics And The Role Of Drp1 In Exercise Performance And Training Adaptations In Skeletal Muscle Sciencedirect



Www Immanuelcollege Net Wp Content Uploads 18 03 P4 Nuclear Fission And Fusion Phys Only Pdf



0wef9qd6mujrpm



Http Mrsgiegler Weebly Com Uploads 5 8 4 0 Fission And Fusion Answers Pdf



Www Ipcc Ch Site Assets Uploads 18 02 Ipcc Wg3 Ar5 Chapter7 Pdf




Ch40 Nuclear Fissionandfusion



2




0wef9qd6mujrpm



Http Www Angelfire Com Fl4 Kevin Physics2 Ch40f Pdf



Www Osti Gov Servlets Purl



2




Mitochondrial Dynamics Mitochondrial Fission And Fusion In Human Diseases Nejm



Iopscience Iop Org Book 978 0 7503 2719 0 Pdf



Nuclear Energy Systems Springerlink
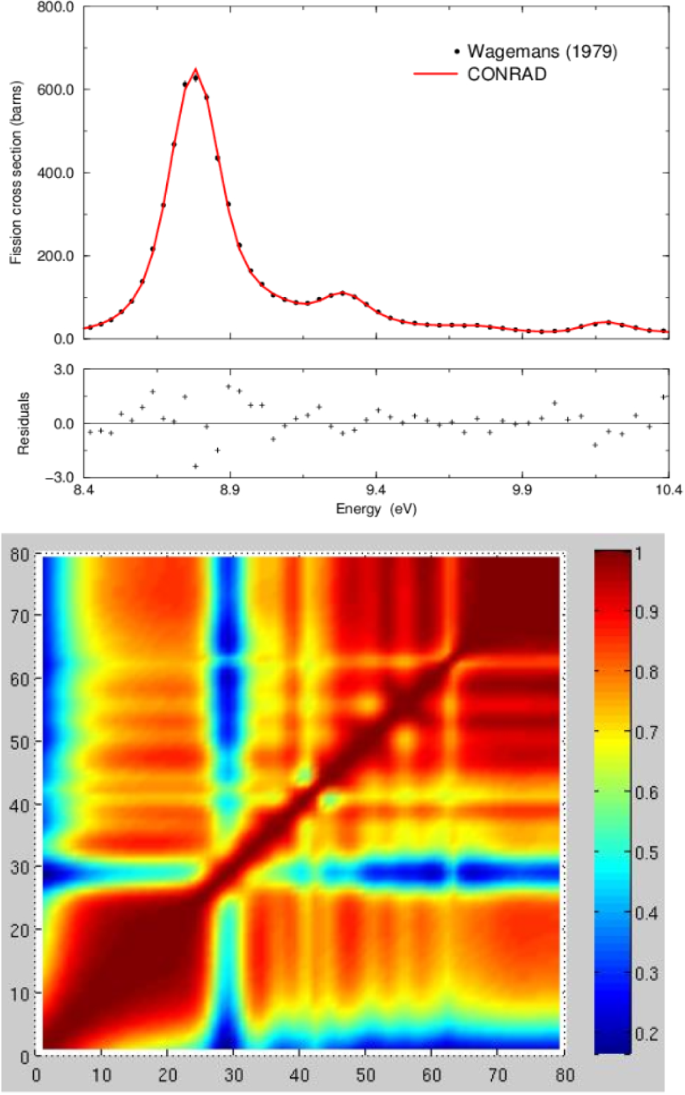



The Joint Evaluated Fission And Fusion Nuclear Data Library Jeff 3 3 Springerlink




Semi Empirical Mass Formula Wikipedia



21 1 Nuclear Structure And Stability Chemistry



Ch40 Nuclear Fissionandfusion


コメント
コメントを投稿